1. How Coffee Actually Wakes You Up

After that first sip, a battle rages between drowsiness and alertness in your body.
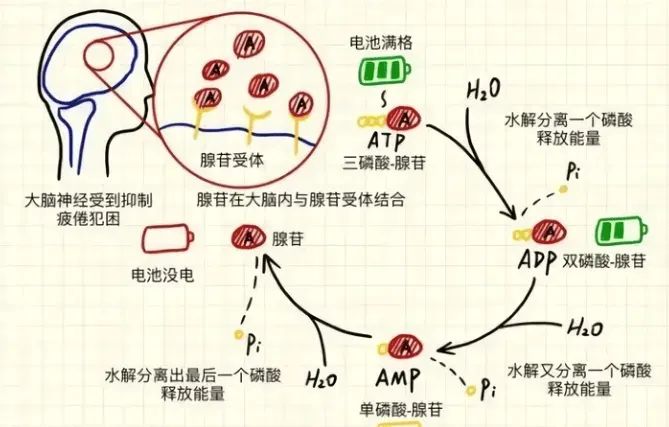
- Your fatigue comes from adenosine – the more it builds, the sleepier you feel.
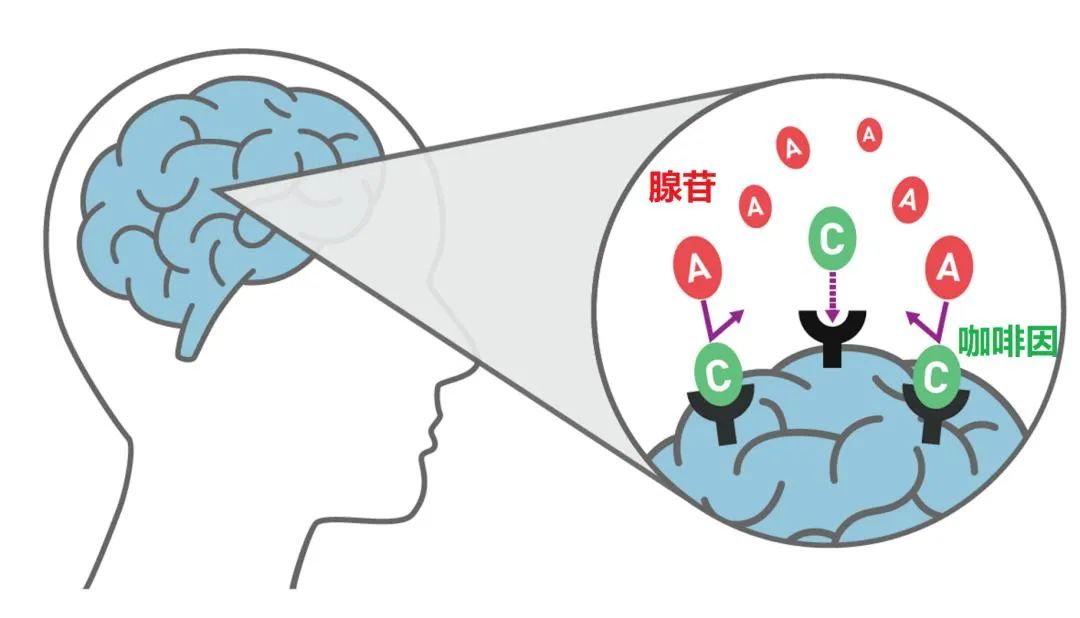
- Caffeine mimics adenosine molecules, blocking receptors and halting sleep signals.
- Simultaneously triggers adrenaline and dopamine releases, creating the “I can conquer this spreadsheet” illusion.
⚠️ Key caveat: Caffeine takes 20 minutes to kick in (European Journal of Neuroscience, 2016). That post-coffee slump? It’s accumulated adenosine hitting back twice as hard.
2. The Power of the “Coffee Nap”

Maximize coffee’s impact with this strategic protocol:
- 0min: Down your coffee → caffeine starts brain infiltration.
- 0-15min: Close eyes → brain clears adenosine during “power nap.”
- 20min: Caffeine arrives + lower adenosine = Peak performance mode.
Hiroshima University (2017) found this combo boosts reaction speed by 150% and cuts errors by 50% compared to coffee-only or nap-only groups.
💡 Office workers: Try post-lunch black coffee (100-150mg) + 15min timer. No sleep? No problem – rest still clears adenosine.
3. Who Should Avoid Coffee?
Slow Metabolizers
Half of young adults process caffeine 8x slower due to the CYP1A2 gene variant. That 3pm latte? You’ll still be counting sheep at 3am.
Self-test: If afternoon coffee delays sleep >30min, you likely have this variant. Stick to pre-noon caffeine if necessary.
Health Conditions to Consider
- High Blood Pressure: Caffeine constricts blood vessels – 300mg can raise BP by 15mmHg
- Anxiety/Depression Meds: Caffeine reduces drug efficacy and worsens anxiety symptoms
- Acid Reflux: Caffeine relaxes stomach sphincters, causing “coffee heartburn”
Dangerous Drug Interactions

- Antibiotics (e.g., Ciprofloxacin): May increase caffeine potency 5x
- Birth Control Pills: Prolong caffeine’s effects to 12 hours
⛔ Avoid coffee 48h pre-surgery and during menstruation.
Smart Coffee Use Guide

- Morning People: Wait 1h post-wake (avoids cortisol peak) for 30% better alertness
- Night Owls: 20min coffee nap > 3 cups of joe
- Sensitive Systems: Try decaf or peppermint iced tea for milder boosts
Remember: Coffee isn’t magic – it’s borrowing alertness from your future self. Prioritize sleep for true energy renewal!
